Delhi Air Pollution 2025: Causes, Effects, AQI Crisis & Long-Term Solutions
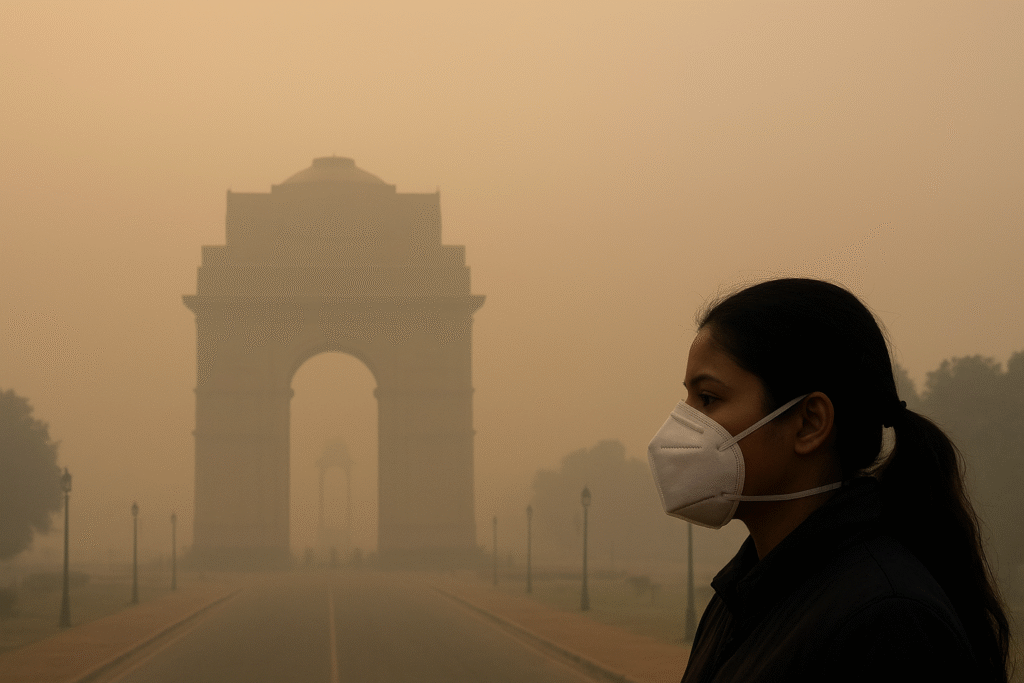

Delhi, India’s capital, known for its cultural heritage and political influence, now makes headlines for a far more dangerous reason—toxic air. Every winter, Delhi turns into a smog-covered city where breathing becomes a challenge. The sky looks grey, roads disappear in haze, and its people—especially children and elders—struggle with coughing, wheezing, and burning eyes.
This article is an expanded deep-dive into Delhi’s air pollution crisis—why it happens, how it affects millions, and what solutions can actually work.
1. Understanding Delhi’s Air Pollution Crisis
Delhi’s air pollution is a result of multiple factors accumulating at the same time. In summer, the pollution is moderate, but once October begins, the city starts drowning in smog due to:
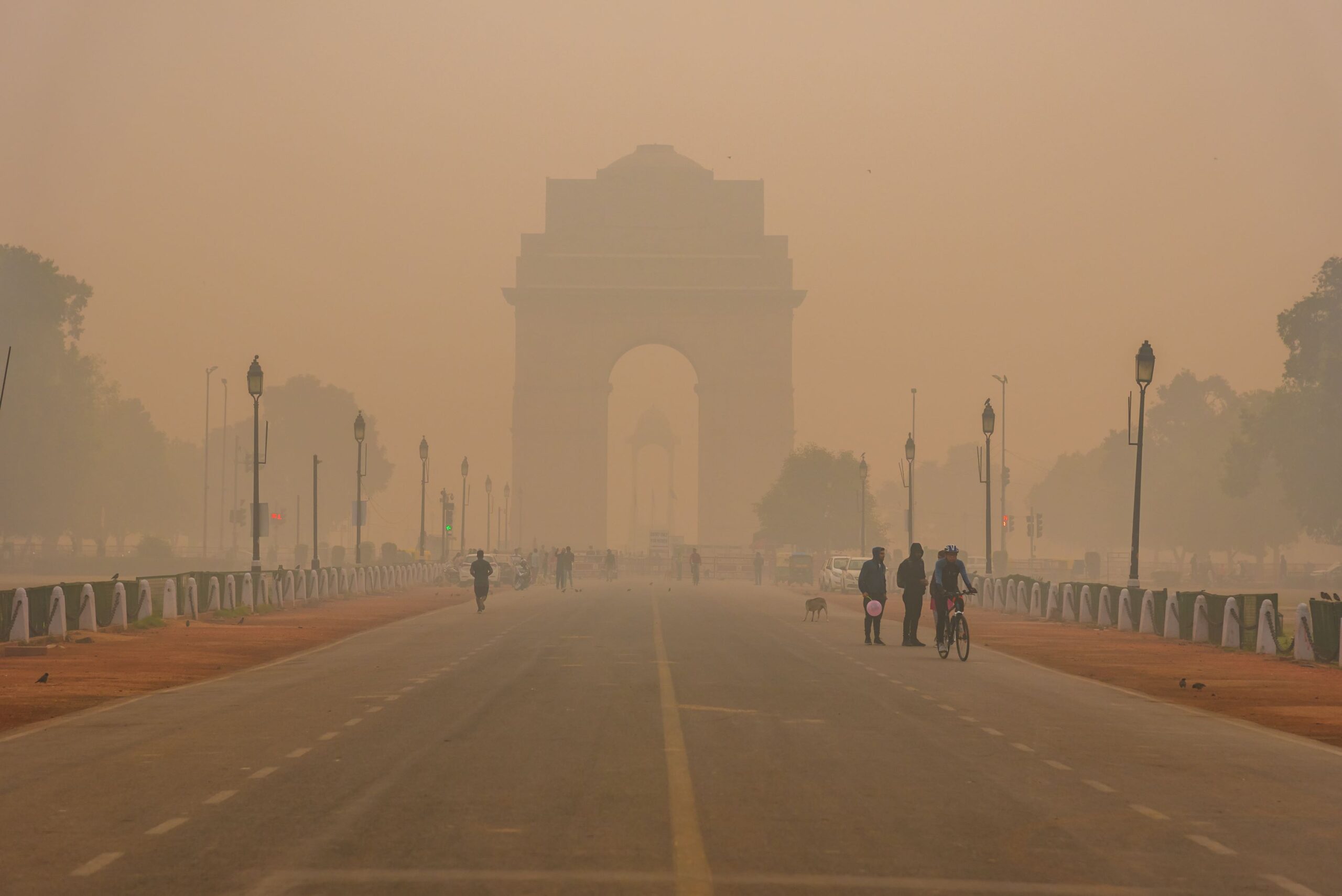

- Slow wind movement
- Temperature drop
- Increased vehicle usage
- Festivals like Diwali
- Construction activity
- Stubble burning
The biggest threat is PM2.5, ultra-fine particles that enter the lungs and bloodstream, causing long-term harm.
In 2025, several reports highlighted that Delhi remained one of the top 10 most polluted cities globally, with AQI often crossing 500+, which is categorized as hazardous.
2. Major Causes of Delhi Air Pollution
2.1 Stubble Burning in Punjab, Haryana & UP

The most discussed and controversial reason for Delhi’s winter pollution is “parali,” or crop stubble burning.
Farmers burn residue to clear fields quickly for wheat sowing.
This adds huge amounts of PM2.5 and CO2 into the air.
Despite government schemes to promote machines like Happy Seeder and balers, farmers often choose burning because:
- Machines are expensive
- Time for crop preparation is short
- Labour shortages persist
- Burning is free and fast
The wind direction during winter pushes this smoke straight into Delhi.
2.2 Vehicle Emissions – The Everyday Poison
Delhi has more vehicles than Mumbai, Kolkata, and Bengaluru combined.
This includes:

- Cars and SUVs
- Bikes and scooters
- Diesel trucks
- Public transport
- Delivery vehicles
Vehicle emissions contribute significantly to PM2.5, NOx, and carbon monoxide.
Traffic congestion worsens emissions because idling vehicles release more toxic gases.
Electric vehicles have increased in Delhi, but not enough to make a major difference yet.
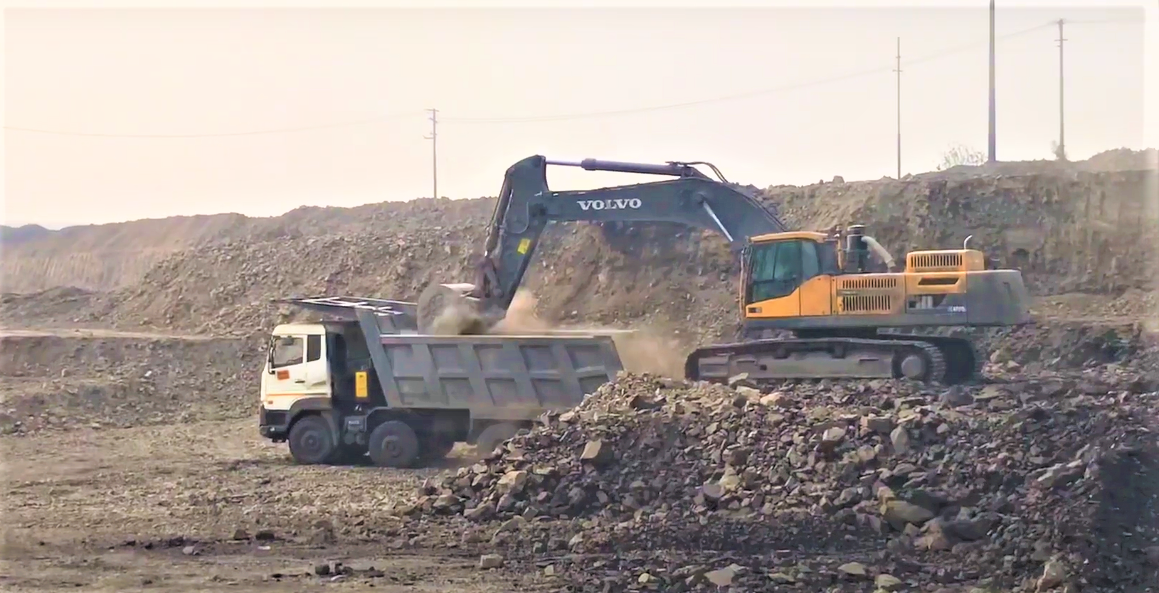
2.3 Construction & Road Dust

Delhi-NCR is always under construction—flyovers, metro lines, expressways, housing societies, malls, and commercial hubs.
The dust from:
- Digging
- Drilling
- Sand movement
- Road widening
- Loading-unloading of materials
creates massive clouds of PM10 particles.
Even when construction bans are imposed, illegal nighttime work continues, worsening the crisis.
2.4 Industrial Emissions
Industrial areas like Bawana, Narela, Okhla, Faridabad, Ghaziabad, and Noida release:

- Chemical fumes
- Burning of rubber and plastic
- Diesel generator smoke
- Waste burning
Many industries still use coal-fired boilers, which emit hazardous smoke into the air.
2.5 Weather Conditions – The Natural Trap
Delhi’s geography traps pollution.
Located inland, with no sea breeze or ventilation, winter conditions worsen the situation.
)
- Wind speed becomes minimal
- Temperature drops sharply
- Pollutants get trapped near the ground
- Fog mixes with smoke → creating smog
This phenomenon is called temperature inversion.
3. Effects of Air Pollution on Health
Delhi’s toxic air has long-term and short-term effects.
3.1 Respiratory Problems
People develop:

- Chronic cough
- Asthma
- Bronchitis
- Allergies
- Reduced lung capacity
Children are especially vulnerable because their lungs are still developing.
3.2 Heart & Brain Disorders
Studies show PM2.5 exposure increases chances of:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- High blood pressure
- Reduced oxygen supply to the brain
Long-term exposure also contributes to cognitive decline.
3.3 Impact on Children
Children breathe faster and spend more time outdoors.
This makes them the biggest victims.
Consequences include:
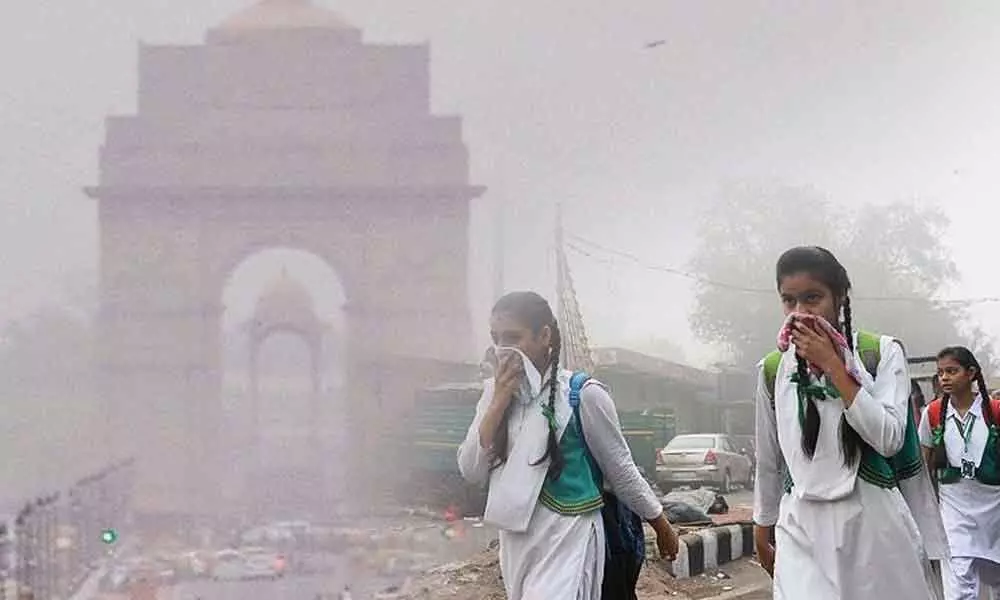

- Weakened immunity
- Early onset asthma
- Learning difficulties
- Lower lung volume
Doctors from AIIMS and Apollo report a 30–40% rise in pediatric respiratory cases every winter.
3.4 Impact on Pregnant Women
Pollution increases risks of:
- Low birth weight
- Premature delivery
- Developmental delays in infants
3.5 Mental Health Effects
Recent studies indicate that smog increases:
- Anxiety
- Mood disorders
- Irritability
- Fatigue
Polluted air reduces the brain’s oxygen supply, impacting concentration and memory.
4. How Delhi Pollution Affects Daily Life
4.1 School Closures
Every winter, Delhi government shuts schools for days or even weeks because pollution hits “severe” level (AQI > 450).
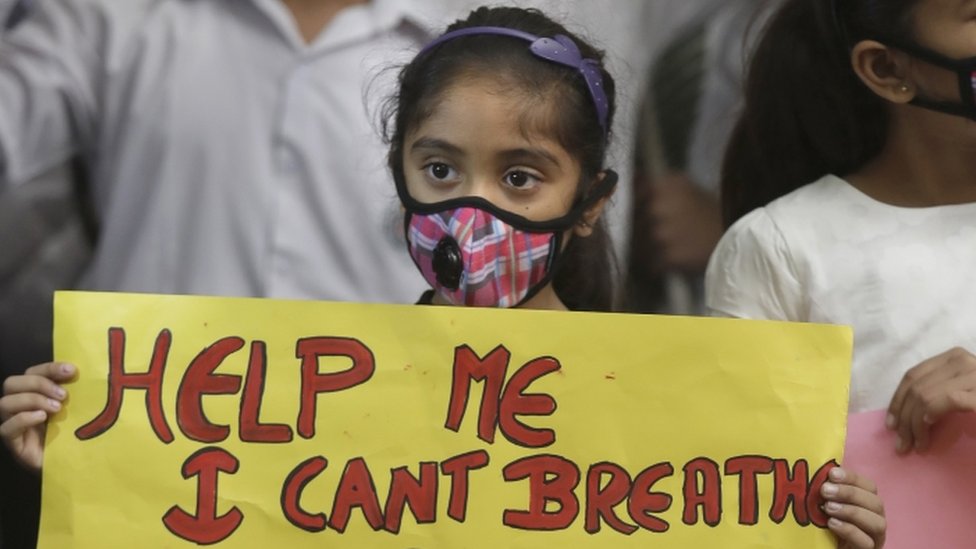
4.2 Flight Diversions & Delays
Visibility decreases drastically, affecting:
- Landing
- Take-off
- Road travel
Smog also leads to traffic accidents.
4.3 Economic Loss
Air pollution reduces:
- Workforce productivity
- Business output
- Outdoor economic activities
India loses nearly ₹15,000 crore annually due to air pollution—Delhi being the biggest contributor.
4.4 Lifestyle Disruptions
- Morning walks are unsafe
- Outdoor sports are stopped
- Jogging or cycling becomes dangerous
People rely heavily on:
- N95 and N99 masks
- Air purifiers
- Nebulizers
- Indoor workouts
5. AQI Levels Explained – How Bad Is Bad?
| AQI Range | Category | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 0–50 | Good | Clean air |
| 51–100 | Satisfactory | Acceptable |
| 101–200 | Moderate | Mild breathing issues |
| 201–300 | Poor | Discomfort |
| 301–400 | Very Poor | Health warnings |
| 401–500 | Severe | Emergency conditions |
| 500+ | Hazardous | Life-threatening |
In peak months, Delhi’s AQI frequently crosses 450–550.
6. Why Government Measures Are Not Enough
6.1 Odd-Even Scheme
Helps temporarily but has no major long-term impact.
6.2 Construction Bans
Often violated; enforcement is weak.
6.3 Anti-Smog Guns
Useful, but limited reach.
6.4 Air Purifiers in Schools
Helps students but does not reduce outdoor pollution.
6.5 Parali Management Schemes
Awareness is still low; many farmers refuse costly machinery.
6.6 Public Transport Limitations
Delhi still needs:
- More buses
- Better last-mile connectivity
- Electric infrastructure
7. Long-Term Solutions: What Can Actually Work?
7.1 Large-Scale EV Adoption
Increase charging stations
Convert buses and govt vehicles to EVs.

7.2 Crop Stubble Solutions
- Subsidizing stubble management machines
- Creating stubble-based industries (biofuel, biogas)
- Government purchase of biomass
7.3 Increase Green Cover
Plant trees along:
- Highways
- Schools
- Industrial zones
- Residential colonies
7.4 Industrial Fuel Conversion
Shift industries from coal/diesel to:
- PNG
- Hydrogen-based fuels
- Solar energy
7.5 Smart Construction Regulations
- Mandatory dust barriers
- Use of pre-mixed concrete
- Strict monitoring systems
7.6 Air Quality Monitoring Expansion
Install more AQI monitors across:
- Schools
- Hospitals
- Residential blocks
Real-time data helps in planning.
8. How Individuals Can Protect Themselves
8.1 Wear Certified Masks
- N95
- N99
- FFP2
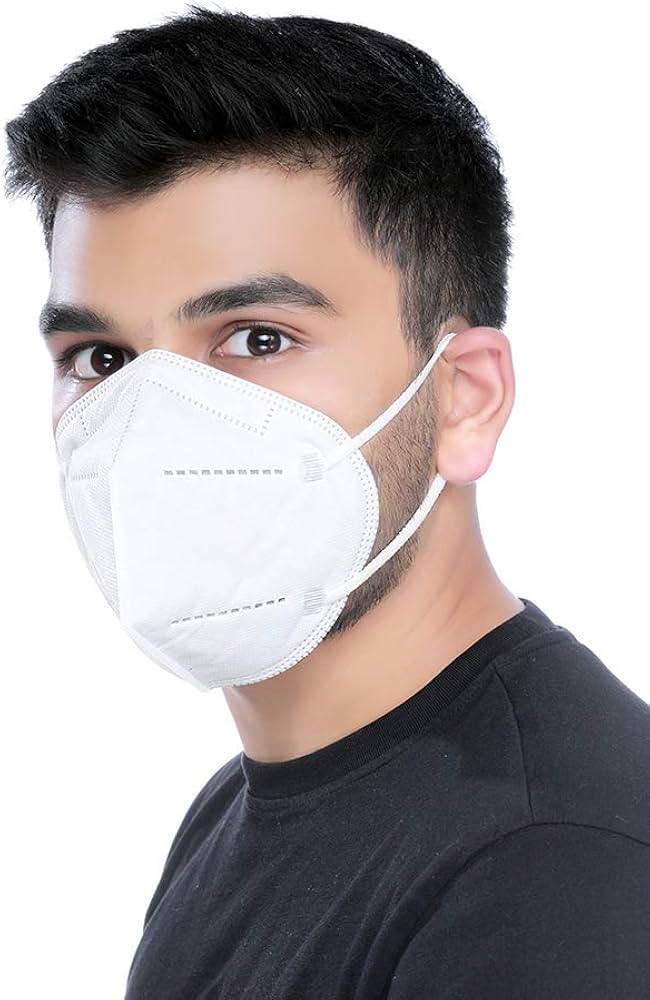

Avoid cloth masks.
8.2 Use Air Purifiers
Especially useful in bedrooms or for kids.
8.3 Exercise Indoors
Avoid outdoor workouts.
8.4 Keep Hydrated
Water helps flush toxins from the body.
8.5 Use Natural Detox Remedies
- Tulsi
- Ginger
- Turmeric
- Vitamin C
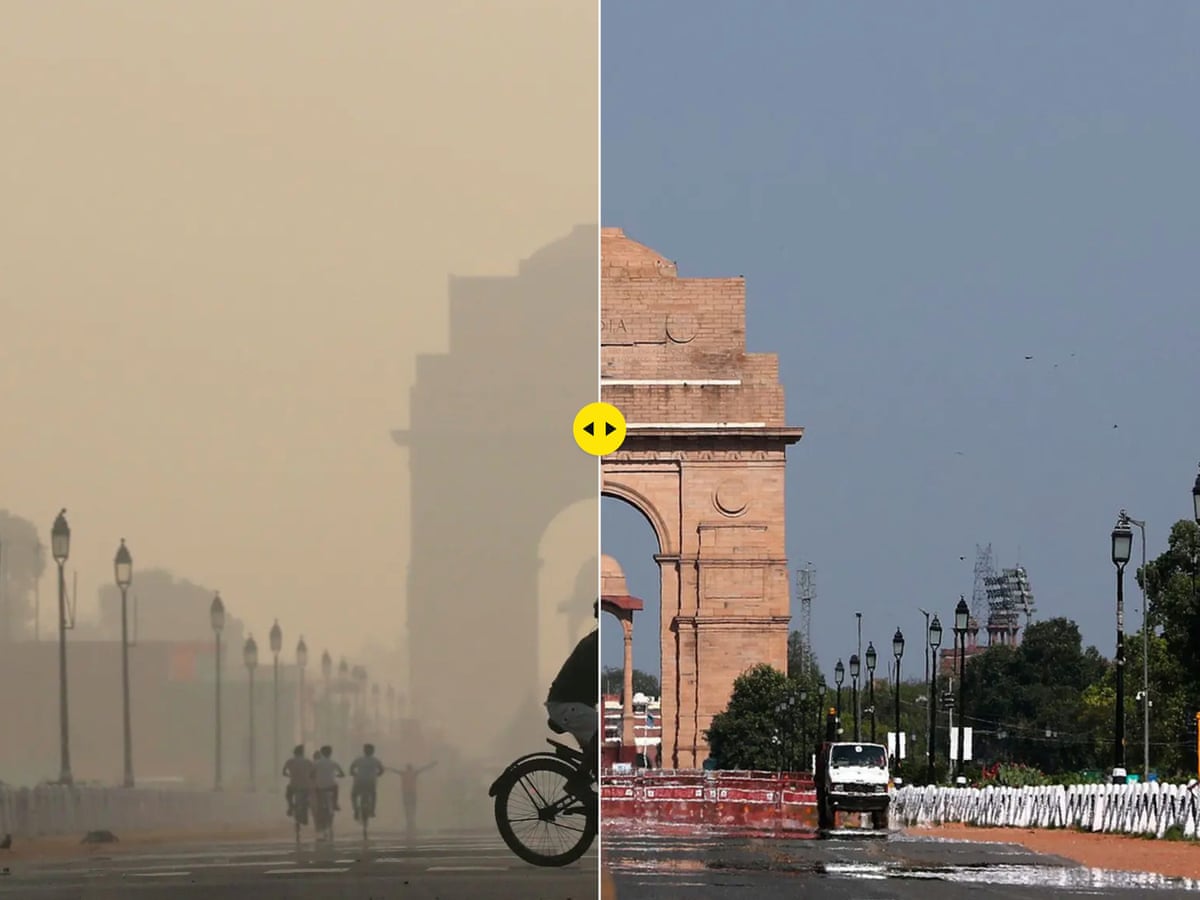
9. Conclusion: The Time to Act Is Now
Delhi’s air pollution problem is not seasonal anymore—it is a year-round public health emergency.
Children, elders, and vulnerable groups are paying the highest price.
While the government has announced multiple schemes, the real change will come from:

- Strong political coordination
- Strict industrial regulation
- Sustainable farming practices
- Public awareness
- Community participation
Delhi deserves clear skies and clean air.
The future of millions depends on the steps we take today.
For More Such Amazing Content Please Visit : https://insightsphere.in/








Post Comment